Microsoft Autorecovery Folder Mac
Note
Office 365 ProPlus is being renamed to Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise. For more information about this change, read this blog post.
Jun 12, 2019 If you are in similar situations, we have the solutions for you. In this article, we will introduce all the fixes on Mac word document recovery, no matter you want to recover unsaved Word document on Mac, or restore lost even retrieve a previous version of Word document on mac in Microsoft Office 2011, 2016 or Office 2019. Mar 19, 2020 I've read in sevral forums that the the autorecover location on Excel 2011 for mac is: /Users/ username /Library/Application Support/ Microsoft/Office/Office 2011 AutoRecovery. However I do not have a Library folder inside 'Username'.
Summary
Microsoft Excel now has a built-in AutoRecover feature that has replaced the AutoSave add-in that exists in versions of Excel that are earlier than Microsoft Excel 2002. The AutoRecover feature saves copies of all open Excel files at a user-definable fixed interval. The files can be recovered if Excel closes unexpectedly, for example, during a power failure.
This article contains an overview of the AutoRecover feature.
More Information
How to configure the AutoRecover settings
Microsoft Office Excel 2007 and Excel 2010
The controls to configure the AutoRecover feature are in the Save settings in Excel Options.
Note To open the Save settings, click the Microsoft Office Button in Excel 2007 or the File menu in Excel 2010, clickExcel Optionsin 2007 or Options in Excel 2010, and then click Save.
To configure the AutoRecover settings, follow these steps:
Under Save Workbooks, click to select the Save AutoRecover info everycheck box to turn on the AutoRecover feature.
In the minutes box, you can type any integer from 1 through 120. This box sets the number of minutes that will occur between saves.
The default is 10 minutes.
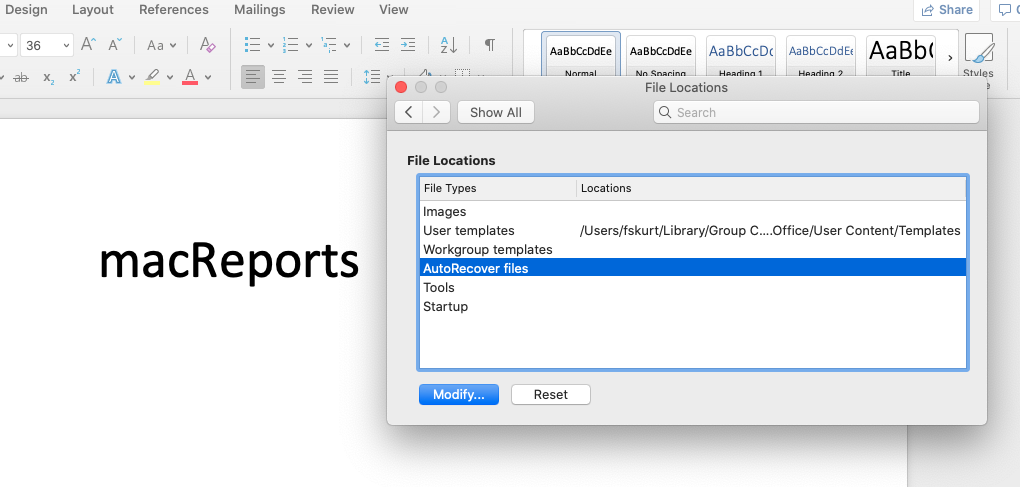
In the AutoRecover file location box, you can type the path and the folder name of the location in which you want the AutoRecover files to stay.
The default location is as follows:
drive:Documents and Settings*user_name*Application DataMicrosoftExcel
Notes
If the location that you type is local (on your hard drive) or is on a network drive, and if this location does not exist, you receive the following error message:
Cannot access directory path.
To determine the unique number that is associated with the message that you receive, press CTRL+SHIFT+I. The following number appears in the lower-right corner of this message:
100100
If you click to clear the AutoRecover file location box but do not enter a new location, AutoRecover files will continue to be saved to the location that you cleared. This will occur until you type a new location.
The AutoRecover file location box remains empty until you type a new location.
You can turn off the AutoRecover feature in an individual workbook. To do this, click to select the Disable AutoRecover for this workbook only check box under the AutoRecover exceptions for box. Make sure that the workbook name is selected in the AutoRecover exceptions for box.
Microsoft Office Excel 2003 and earlier versions of Excel
The controls to configure the AutoRecover dialog box are on the Save tab of the Options dialog box.
Note To open the Options dialog box, click Options on the Tools menu.
To configure the AutoRecover dialog box, follow these steps:
Under Settings, click to select the Save AutoRecover info everycheck box to turn on the AutoRecover feature.
In the minutes box, you can type any integer from 1 through 120. This box sets the number of minutes that will occur between saves.
The default is 10 minutes.
In the AutoRecover file location box, you can type the path and the folder name of the location in which you want the AutoRecover files to stay.
The default location is as follows:
drive:Documents and Settings*user_name*Application DataMicrosoftExcel
Notes
If the location that you type is local (on your hard drive) and if the location does not exist, you receive the following error message:
Cannot access directory path.
If the location that you type is on a network drive, you will not receive an alert until your first AutoRecover attempt. You receive the following error message:
Microsoft cannot save AutoRecover info to path. Please check the network connection or change the location on the Save tab of the Tools, Options dialog.
If you clear the AutoRecover file location box but do not enter a new location, AutoRecover files will continue to be saved to the location that you cleared. This occurs until you type a new location.
The AutoRecover file location box remains empty until you type a new location.
You can turn off the AutoRecover feature in an individual workbook. To do this, click to select the Disable AutoRecover check box under Workbook options.
When an AutoRecover event is triggered
When an Excel file is open and AutoRecover is turned on, AutoRecover does not save the file until the first change is made to the file, the AutoRecover save time interval passes, and Excel has been idle for some time (the default is 30 seconds). After AutoRecover saves the file, the file is only saved at subsequent save intervals if further changes are made.
When AutoRecover files are deleted
To keep from filling up your AutoRecover location with unneeded files, AutoRecover files are automatically deleted in the following situations:
- When the file is manually saved.
- The file is saved with a new file name using Save As.
- You close the file.
- You quit Excel, whether you choose to save the file or not.
- You turn off AutoRecover for the current workbook.
- You turn off AutoRecover by clearing the Save AutoRecover info every check box.
AutoRecover save timing
The AutoRecover timer checks for changed Excel files at the interval you set in the minutes box on the Save tab in the Options dialog box. The timer starts when you start Excel.
Note
In Excel 2007, the minutes box is in the Save category in the Excel Option dialog box. In Excel 2010, the minutes box is in the Save category under File, Options.
When the first save interval passes, Excel checks to see whether any open files have been changed. If Excel locates changed files, an idle timer starts. The purpose of the idle timer is to make sure that the user does not make entries in the worksheet while the save operation occurs. The idle timer restarts each time that the user makes an entry into the worksheet so the AutoRecover save file is not created until both the save interval passes and no entries are made for the duration of the idle time.
The default idle time is 30 seconds. To change the default idle time, use the AutoRecoverDelay registry key. To do this, follow these steps.
Important This section, method, or task contains steps that tell you how to modify the registry. However, serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly. Therefore, make sure that you follow these steps carefully. For added protection, back up the registry before you modify it. Then, you can restore the registry if a problem occurs. For more information about how to back up and restore the registry, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
322756 How to back up and restore the registry in Windows
Quit Excel if it is running.
Click Start, click Run, type regedit in the Open box, and then click OK.
Locate and then select one of the following registry keys, as appropriate for the version of Excel that you are running.
For Microsoft Excel 2002:
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftOffice10.0ExcelOptions
For Excel 2003:
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftOffice11.0ExcelOptions
For Excel 2007:
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftOffice12.0ExcelOptions
For Excel 2010:
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftOffice14.0ExcelOptions
On the Edit menu, click New, and then click DWORD value.
Type the following name for the new value:
AutoRecoverDelay
Press ENTER.
Right-click the AutoRecoverDelay registry key, and then click Modify.
In the Value data box, type a number between 1 and 600. This is the number of seconds before AutoRecover tries to save.
When you are finished, click OK.
Quit Registry Editor.
Note
Only manually performed actions in the program affect the idle timer. Formulas that automatically update the file do not affect the idle timer. Excel saves the file when the idle time is reached, between the automatic updates to the formulas.
File formats that are saved by AutoRecover
AutoRecover saves all file formats that can be opened in Excel. To maintain speed and simplicity, AutoRecover saves all files as the current Excel file format, regardless of the original file format opened. The file is saved as a hidden file with an arbitrary filename with the extension .xar (for example, ~ar18a.xar).
When you try to save a recovered file upon reopening Excel after it closed unexpectedly, the original file format and name is suggested as the Save file type. Excel stores the original file name and its related .xar file name in the registry for the purpose of recovery.
AutoRecover and multiple instances of Excel
When more than one instance of Excel is running and one instance closes unexpectedly, a new instance of Excel is automatically started and the AutoRecover files are opened. If all instances of Excel close unexpectedly, but the computer is still running, a single instance of Excel is started and all AutoRecover files are opened. In the case of a power outage, all recovered files are opened when you start Excel again.
Compatibility
All AutoRecover settings, except the Disable AutoRecover workbook option, are stored in the system registry. AutoRecover settings are compatible with files from previous versions of Excel is not an issue.
When the Disable AutoRecover workbook option is set, and the file is opened in an earlier version of Excel, saved, and then reopened in a later version of Excel, the Disable AutoRecover workbook option is not affected.
References
For more information about how to troubleshoot errors when you save Excel files, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
271513 How to troubleshoot errors when you save Excel files
-->Note
Office 365 ProPlus is being renamed to Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise. For more information about this change, read this blog post.
If you're looking for recent Word document recovery info, see:
- Recover your Office files (For versions through Office 2019)
For more on earlier versions of Word, see:
Resolution
To fix this problem, use the following methods in the order in which they're presented, as appropriate for your situation.
Method 1: Search for the original document
To do this, follow these steps, as appropriate for the version of Windows that you're running.
Windows 10 and Windows 7
- Select Start, type the document name in the Start Search box (.doc or .docx), and then press Enter. If the File list contains the document, double-click the document to open it in Word.
- If the File list does not contain the file, go to Method 2.
Method 2: Search for Word backup files
Word backup file names end with the .wbk extension. If the Always create backup copy option is selected, there may be a backup copy of the file.
Note
To locate this option:
- Word for Office 365, Word 2019, Word 2016, and Word 2013:Select File, then Options, and then Advanced. Scroll down to the Save section and select Always create backup copy.
- Word 2010:Select File, then Options. In the Save tab, select Always create backup copy.
To find the backup copy of the file, follow these steps:
- Locate the folder in which you last saved the missing file.
- Search for files that have the .wbk file name extension.
If there's no .wbk file in the original folder, search the computer for any .wbk files. To do this, follow these steps:
Windows 10 and Windows 7
- Select Start, type *.wbk in the Start Search box, and then press Enter.
- If the File list contains the backup file, repeat the steps in step 2 ('Search for files that have the .wbk file name extension') to open the file. If the File list does not contain the backup file, go to Method 3.
If you find any files that have the name 'Backup of' followed by the name of the missing file, use one of the following procedures, as appropriate for the version of Word that you're running.
Word for Office 365, Word 2019, Word 2016, and Word 2013
- On the File menu, select Open, and then Browse. (In some versions, select Computer and then Browse.)
- In the Files of type list (All Word Documents), select All Files.
- Select the backup file that you found, and then select Open.
Word 2010
- On the File menu, select Open.
- In the Files of type list (All Word documents), select All Files.
- Select the backup file that you found, and then select Open.
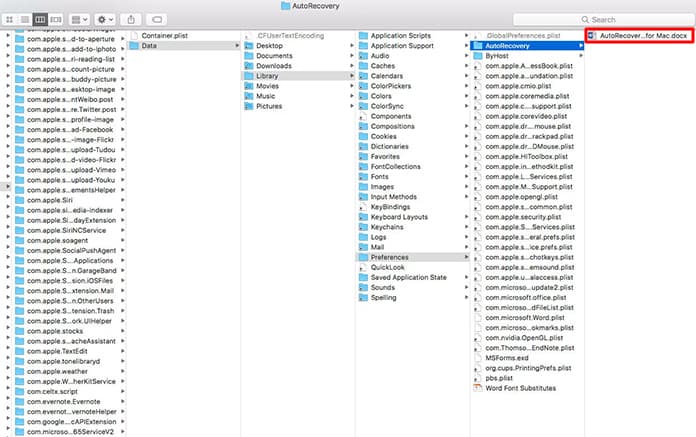
Method 3: Search for AutoRecover files
AutoRecover file names end with the .asd extension. By default, Word searches for AutoRecover files every time that it starts, and then it displays all that it finds in the Document Recovery task pane.
Use Word to automatically find the AutoRecover files. To do this, follow these steps:
Right-click the taskbar, and then select Task Manager.
On the Processes tab, select any instance of Winword.exe or Microsoft Word, and then select End Task or End Process. Repeat this step until you have exited all instances of Winword.exe and Word.
Close the Windows Task Manager dialog box, and then start Word.
If Word finds the AutoRecover file, the Document Recovery task pane opens on the left side of the screen, and the missing document is listed as 'document name [Original]' or as 'document name [Recovered].' If this occurs, double-click the file in the Document Recovery pane, select Save As on the File menu, and then save the document as a .docx file. Manually change the extension to .docx, if necessary, by right-clicking the file and selecting Rename.
If the Recovery pane does not open, manually search for AutoRecover files. To do this, use one of the following procedures, as appropriate for the version of Word that you're running.
Word for Office 365, Word 2019, Word 2016, and Word 2013
- On the File menu, select Open, and then Browse.
- If you don't see your document listed, select Recover Unsaved Documents.
Word 2010
- On the File menu, select Recent.
- If you don't see your document listed, select Recover Unsaved Documents.
If you can't locate an AutoRecover file in the location that is identified in the Folder name list, search your whole drive for any .asd files. To do this, follow these steps:
Windows 10 and Windows 7
- Select Start, type .asd in the Start Search box, and then press Enter.
- If the File list does not contain AutoRecover files, go to Method 4.
If you find any files that have the .asd extension, use one of the following procedures, as appropriate for the version of Word that you're running:
Word 2019, Word 2016, or Word 2013
- On the File menu, select Open, and then Browse. (In some versions, select **Computer **and then Browse.)
- In the Files of type list (All Word Documents), select All Files.
- Select the .asd file that you found, and then select Open.
Word 2010
- On the File menu, select Open.
- In the Files of type list (All Word Documents), select All Files.
- Select the .asd file that you found, and then select Open.
Note
If you find an AutoRecover file in the Recovery pane that does not open correctly, go to 'Method 6: How to troubleshoot damaged documents' for more information about how to open damaged files.
Method 4: Search for temporary files
Temporary file names end with the .tmp extension. To find these files, use one of the following procedure.
Windows 10 and Windows 7
- Select Start, type .tmp in the Start Search box, and then press Enter.
- On the Show only toolbar, select Other.
- Scroll through the files and search for files that match the last few dates and times that you edited the document. If you find the document that you're looking for, go to 'Method 6: How to troubleshoot damaged documents' for more information about how to recover information from the file.
Method 5: Search for '~' files
Some temporary file names start with the tilde (~) character. To find these files, follow these steps:
Windows 10 and Windows 7
Select Start, type ~ in the Start Search box.
Select See more results.
Scroll through the files, and look for any that may match the last few dates and times that you edited the document. If you find the document that you're looking for, go to 'Method 6: How to troubleshoot damaged documents' for more information about how to recover information from the file.
For information about how Word creates and uses temporary files, see Description of how Word creates temporary files.
Method 6: How to troubleshoot damaged documents
For information about how to troubleshoot damaged Word documents, see the following articles in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
More information
You can lose a Word document in certain situations. For example, the document may be lost if an error occurs that forces Word to close, if you experience a power interruption while editing, or if you close the document without saving your changes.
Note
The whole document may be lost if you have not recently saved the document. If you have saved your document, you may lose only the changes that you made since the last save. Be aware that some lost documents may not be recoverable.
Microsoft Autorecovery Folder Mac Command
The AutoRecover feature in Word performs an emergency backup of open documents when an error occurs. Some errors can interfere with the AutoRecover functionality. The AutoRecover feature is not a substitute for saving your files.
Microsoft Autorecovery Folder Mac Pro
We do not provide any utilities to recover deleted documents. However, some third-party utilities to recover deleted documents might be available on the Internet.
For more information about AutoRecover, see the following articles in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
The third-party products that are discussed in this article are manufactured by companies that are independent of Microsoft. Microsoft makes no warranty, implied or otherwise, regarding the performance or reliability of these products.




